|
Characteristics
|
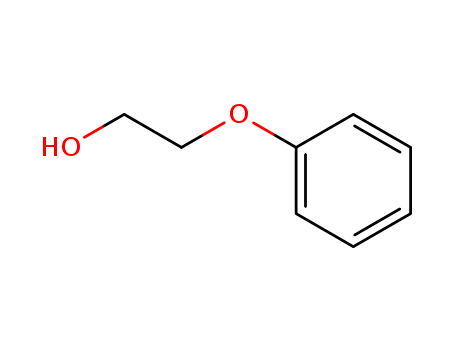
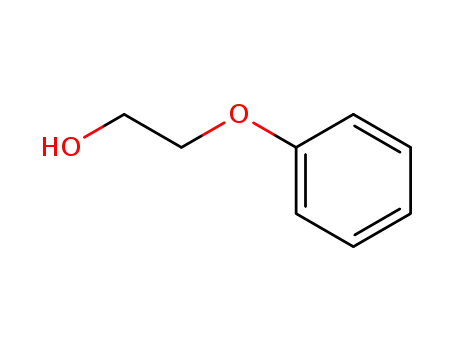
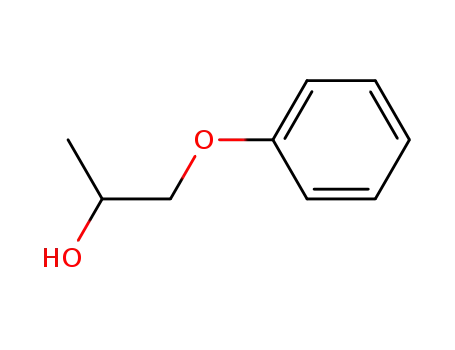
Phenoxyethanol is a tried-and-tested preservative, which is welltolerated by the skin and has a low allergy risk. It can be used over a wide pH range. This means that other preservatives can lose their effectiveness if the product is not within the right pH range. It does not smell unpleasant or change the color of the product, which can be the case when using natural antimicrobial substances.
|
|
Production Methods
|
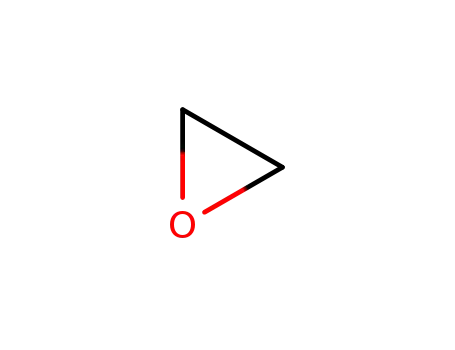
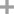
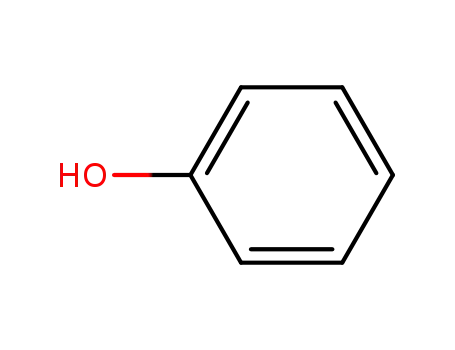
Phenoxyethanol is prepared by treating phenol with ethylene oxide in an alkaline medium.
|
|
Synthesis Reference(s)
|
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 40, p. 1356, 1975 DOI: 10.1021/jo00897a043
|
|
General Description
|
Colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Density 1.02 g / cm3. An irritant.
|
|
Air & Water Reactions
|
Oxidizes in air to form unstable peroxides that may explode spontaneously [Bretherick, 1979 p.151-154, 164]. Water soluble.
|
|
Reactivity Profile
|
2-Phenoxyethanol may react violently with strong oxidizing agents. May generate flammable and/or toxic gases with alkali metals, nitrides, and other strong reducing agents. May initiate the polymerization of isocyanates and epoxides.
|
|
Health Hazard
|
May cause moderate eye irritation and moderate corneal injury. Excessive exposure may cause skin irritation and hemolysis.
|
|
Fire Hazard
|
2-Phenoxyethanol is combustible.
|
|
Flammability and Explosibility
|
Notclassified
|
|
Pharmaceutical Applications
|
Phenoxyethanol is an antimicrobial preservative used in cosmetics and topical pharmaceutical formulations at a concentration of 0.5–1.0%; it may also be used as a preservative and antimicrobial agent for vaccines.Therapeutically, a 2.2% solution or 2.0% cream has been used as a disinfectant for superficial wounds, burns, and minor infections of the skin and mucous membranes. Phenoxyethanol has a narrow spectrum of activity and is thus frequently used in combination with other preservatives,
|
|
Industrial uses
|
2-Phenoxyethanol is used as a preservative in cosmetic formulations at a maximum concentration of 1.0%. 2-Phenoxyethanol is a broad spectrum preservative which has excellent activity against a wide range of Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, yeast and mould. It is also used as a solvent and, because of its properties as a solvent, it is used in many blends and mixtures with other preservatives. 2-Phenoxyethanol is not registered as a food additive in the EU. Scognamiglio et al. (ref. 105) reported that 2-phenoxyethanol is a fragrance ingredient used in many fragrance mixtures (see discussion). An ester of 2-Phenoxyethanol, 2-Phenoxyethyl isobutyrate and 2-Phenoxyacetic acid, the main metabolite of 2-Phenoxyethanol, were mentioned in a WHO publication where 43 flavouring agents in food were evaluated (WHO 2003, AR4), however at intakes assessed to be very low in Europe (around 1 μg/kg bw/day).
|
|
Contact allergens
|
Phenoxyethanol is an aromatic ether-alcohol used mainly as a preservative, mostly with methyldibromoglutaronitrile (in Euxyl? K 400) or with parabens. Sensitization to this molecule is very rare.
|
|
Safety Profile
|
Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. A skin and severe eye irritant. Mutation data reported. Some glycol ethers have dangerous human reproductive effects. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. To fight fEe, use CO2, dry chemical. Used as a solvent for ester-type resins. See also GLYCOL ETHERS.
|
|
Safety
|
Phenoxyethanol produces a local anesthetic effect on the lips, tongue, and other mucous membranes. The pure material is a moderate irritant to the skin and eyes. In animal studies, a 10% v/v solution was not irritant to rabbit skin and a 2% v/v solution was not irritant to the rabbit eye.Long-term exposure to phenoxyethanol may result in CNS toxic effects similar to other organic solvents.Safety issues related to preservatives used in vaccines, including 2-phenoxyethanol have been reviewed.Contact urticaria has been reported upon exposure to 2-phenoxyethanol-containing cosmetics. The US FDA has recommended avoiding at least one topical product containing phenoxyethanol due to concerns over inadvertant exposure to nursing infants. LD50 (rabbit, skin): 5 g/kg LD50 (rat, oral): 1.26 g/kg
|
|
storage
|
Aqueous phenoxyethanol solutions are stable and may be sterilized by autoclaving. The bulk material is also stable and should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
|
|
Incompatibilities
|
The antimicrobial activity of phenoxyethanol may be reduced by interaction with nonionic surfactants and possibly by absorption by polyvinyl chloride.The antimicrobial activity of phenoxyethanol against Pseudomonas aeruginosa may be reduced in the presence of cellulose derivatives (methylcellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and hypromellose (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose)).
|
|
Regulatory Status
|
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Under European regulations for cosmetics (76/768/EEC), the maximum authorized concentration (MAC) of 2-phenoxyethanol is 1.0%.
|
|
Consumer Uses
|
This substance is used in the following products: lubricants and greases, polishes and waxes, adhesives and sealants, coating products, fillers, putties, plasters, modelling clay, anti-freeze products, washing & cleaning products and cosmetics and personal care products. Other release to the environment of this substance is likely to occur from: indoor use (e.g. machine wash liquids/detergents, automotive care products, paints and coating or adhesives, fragrances and air fresheners), outdoor use, indoor use in close systems with minimal release (e.g. cooling liquids in refrigerators, oil-based electric heaters) and outdoor use in close systems with minimal release (e.g. hydraulic liquids in automotive suspension, lubricants in motor oil and break fluids).
|
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego