|
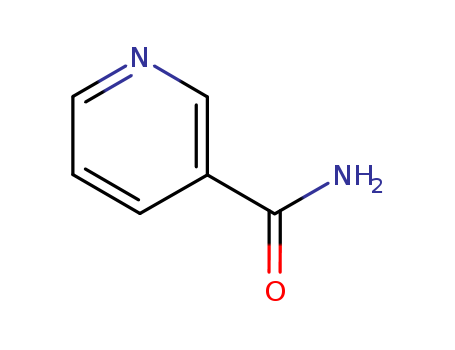
Amide Analog of Vitamin B3
|
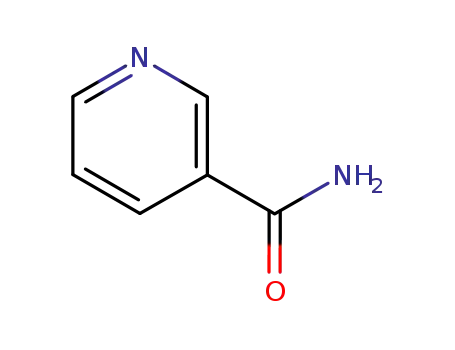
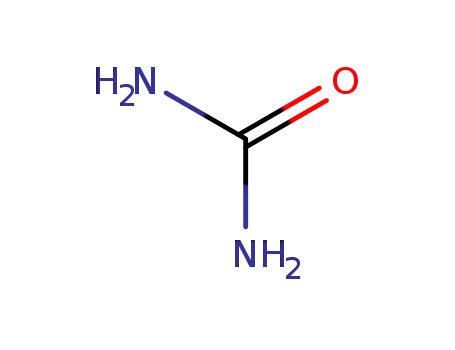
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is an amide form of vitamin B3. It is a precursor of essential coenzymes required for various reactions in the body, including the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
|
|
Management of Skin Disorders
|
Niacinamide is now explored for its potential in managing various skin disorders. It has been used topically in the treatment of acne vulgaris, melasma, atopic dermatitis, and rosacea.
|
|
Inhibition of Sirtuins
|
At high doses, niacinamide acts as a dietary supplement that inhibits sirtuins, a class of enzymes involved in cellular regulation.
|
|
Water-Soluble Amide Derivative
|
Niacinamide is a water-soluble amide derivative of nicotinic acid (niacin), which is one of the major forms of vitamin B3. The recommended dietary allowance for vitamin B3 in adults is typically 14 to 16 mg daily.
|
|
Safety and Tolerance
|
Niacinamide is generally well-tolerated and has been widely used in cosmetic and personal care formulations for various skin conditions. It is considered an inexpensive dietary supplement that is readily available to the public.
|
|
Topical Formulations
|
Niacinamide is commonly found in topical formulations for skincare. Studies have confirmed its permeation under certain conditions, indicating its potential effectiveness when applied to the skin.
|
|
description
|
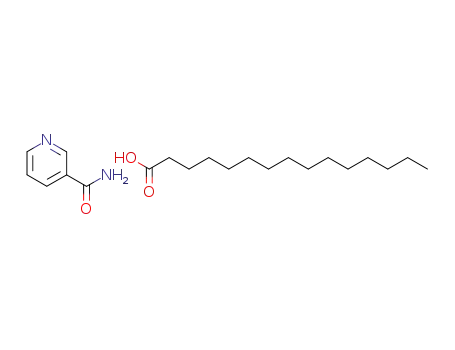
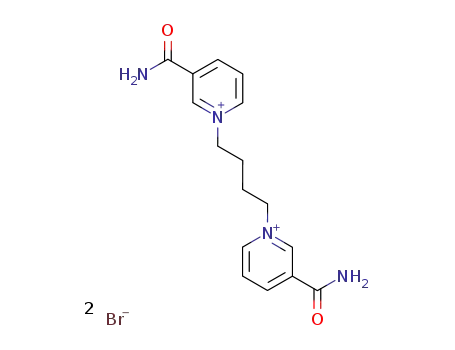
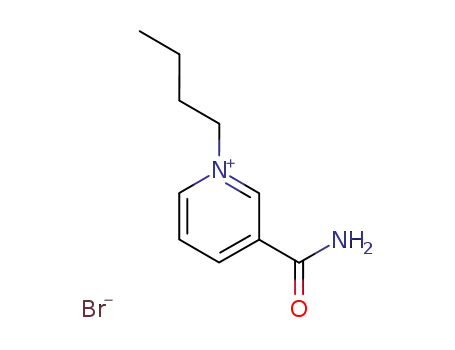
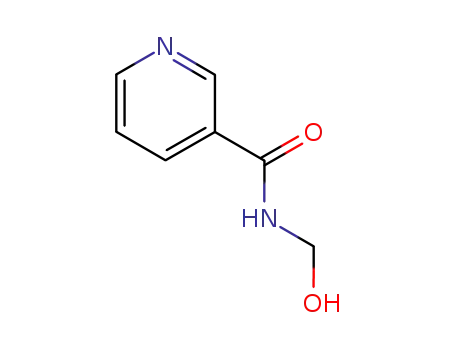
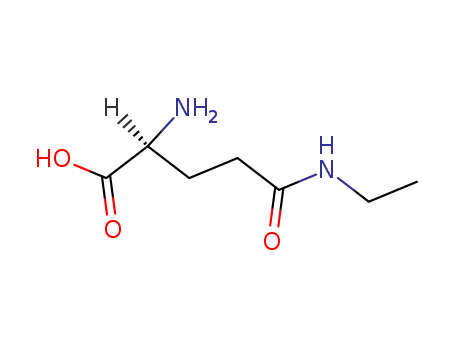
Nicotinamide aka Vitamin B3 (niacinamide, nicotinic acid amide) is the pyridine 3 carboxylic acid amide form of niacin. It is a water?soluble vitamin that is not stored in the body. The main source of vitamin in diet is in the form of nicotinamide, nicotinic acid, and tryptophan. The main source of niacin include meat, liver, green leafy vegetables, wheat, oat, palm kernel oil, legumes, yeast, mushrooms, nuts, milk, fish, tea, and coffee.The recommended daily dose of vitamin B3 in niacin equivalent is given in Table 1.Nicotinamide is a component of coenzyme I (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADP) and coenzyme II (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, NADP). The nicotinamide part of these two coenzyme structures in human body has reversible hydrogenation and dehydrogenation characteristics, It plays a hydrogen transfer role in biological oxidation, can promote tissue respiration, biological oxidation process and metabolism, and is of great significance to maintain the integrity of normal tissues, especially skin, digestive tract and nervous system. When lacking, pellagra is caused by the influence of cell respiration and metabolism.
|
|
Toxicity
|
LD50 2.5~3.5 g/kg (rats, through the mouth). GRAS(FDA,§182.5535,2000). ADI is no special regulation (EEC, 1990).
|
|
Synthesis
|
1.β-methyl pyridine is oxidized to nicotinic acid by air, and the latter is produced by the action of ammonium hydroxide, and then heating and dehydration. 2.Nicotinic acid, boric acid and ammonia into reaction pot, stirring at the condition of ammonia gas, heating dissolution; then distilled ammonia recovery, to 120℃ after the immigration dewatering pot continues to enrich; when the temperature reached 145 ℃, start adding liquid ammonia, and in 185 to 190℃ to ammonia reaction 20~30h. And then cooled to 130℃, diluted with distilled water, activated carbon was added, and in 70~80℃through ammonia decolorization 2h; reaction after filtered, , filtrate in 24 hours after analysis of cold water, fractional crystallization and washing with ethanol, and drying to obtain the finished product. The yield was 89%. 3. From the nicotinic acid and ammonia react into salt and then dehydrated.
|
|
Definition
|
ChEBI: A pyridinecarboxamide that is pyridine in which the hydrogen at position 3 is replaced by a carboxamide group.
|
|
Manufacturing Process
|
Gaseous ammonia was passed into nicotinic acid at a temperature between 200-235°C until the conversion to nicotinamide was 85%. The reaction mixture was colored light brown. The reaction mass was cooled and grounds to a fine powder. Fifty grams of this crude nicotinamide were boiled with 500 ml of anhydrous ethyl acetate until a dark solution was. obtained. A little solid remained in suspension. Gaseous ammonia was passed in below the surface of the ethyl acetate at a temperature between 60-70°C. After a short time ammonium nicotinate started to precipitate out of solution as a brown solid. Sufficient gaseous ammonia, was passed into the ethyl acetate solution to insure complete precipitation of the nicotinic acids as ammonium nicotinate. The solution was filtered at about 60-70°C. The filter cake consisted of ammonium nicotinate, which, upon drying, weighed 12.4 grams. The filtrate was stirred arid boiled for 20 minutes with one-half gram of activated carbon and two grams of activated adsorbent clay. The mixture was filtered hot. The filtrate was boiled twenty minutes with one-half gram of activated carbon and two grams of activated adsorbent clay and then filtered hot. The carbon and clay treatment was repeated once more. The final filtrate was cooled slowly with stirring to room temperature to precipitate white crystalline nieocinamide which, upon drying, weighed 26.7 grams and had a melting point of 129.5°C, and was over 99 percent pure. The mother liquor from the above filtration was boiled down to one-third of its volume and cooled to room temperature. A second crop of nicotinamide of three grams was obtained.
|
|
Synthesis Reference(s)
|
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 76, p. 5774, 1954 DOI: 10.1021/ja01651a043Tetrahedron Letters, 36, p. 8657, 1995 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)01785-G
|
|
General Description
|
Vitamin B3 was formerly called nicotinic acid; however, the term niacin is now preferred to avoid any confusion with the alkaloid, nicotine. Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, refers to the amide derivative of niacin that is equivalent in vitamin activity. Some texts use niacin to refer to nicotinic acid, niacinamide, and any derivatives with vitamin activity comparable to niacin. Furthermore, research and chemistry-based resources use the terms nicotinic acid and nicotinamide; whereas pharmacy resources use niacin and niacinamide.
|
|
Air & Water Reactions
|
Water soluble.
|
|
Reactivity Profile
|
An amine and amide. Acts as a weak base in solution. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
|
|
Flammability and Explosibility
|
Nonflammable
|
|
Biochem/physiol Actions
|
Nicotinamide is an amide derivative of vitamin B3 and a PARP inhibitor
|
|
Safety Profile
|
Nicotinamide is a safe and inexpensive compound with negligible side effects. It is well tolerated even in doses of 1g/day to 3g/day.There are no reports of teratogenicity with nicotinamide. Minor side effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue. It does not cause vasodilatory side effects like flushing, alteration in blood pressure, body temperature or pulse as seen with niacin.In topical formulation, it does not cause skin irritation, photosensitization in concentrations of 0.0001% to 4%.
|
|
Potential Exposure
|
Used as a dietary supplement and food additive.
|
|
Metabolism
|
Nicotinamide is ingested in food as part of pyridine nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) in plant and animal tissues. After the co?enzymes have separated, nicotinamide is absorbed almost completely in the small intestine. After absorption, nicotinamide is stored as NAD in the liver and excretion occurs via kidneys. Tryptophan is converted to nicotinamide through kynurenine?anthranilate pathway in the liver. Tryptophan can thus satisfy the requirement for dietary nicotinic acid.
|
|
Purification Methods
|
Crystallise niacin from *benzene. It has solubility in g/ml: H2O (1), EtOH (0.7) and glycerol (0.1). [Methods in Enzymology 66 23 1980, UV: Armarego Physical Methods in Heterocyclic Chemistry (Ed Katritzky, Academic Press) Vol III 83 1971, Beilstein 22 III/IV 389, 22/2 V 80.]
|
|
Incompatibilities
|
Combustible solid; dust may form explosive mixture with air. Amides are incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
|
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego