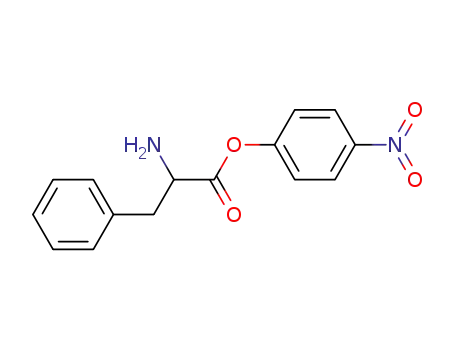
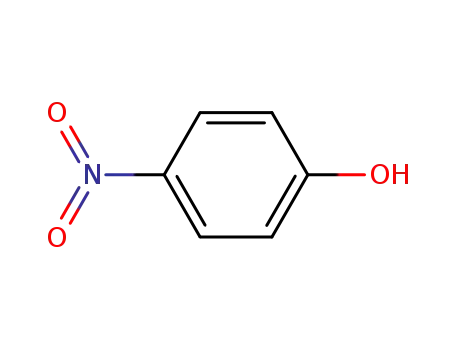
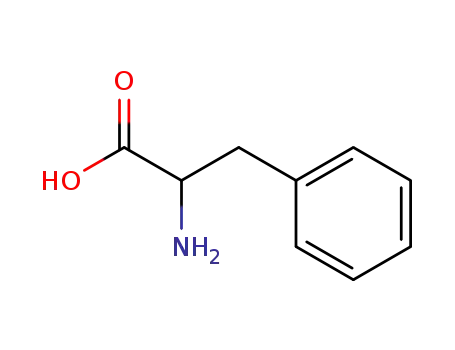
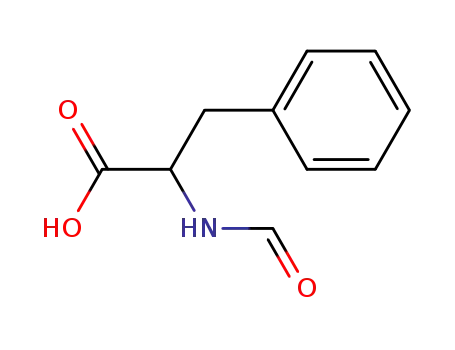
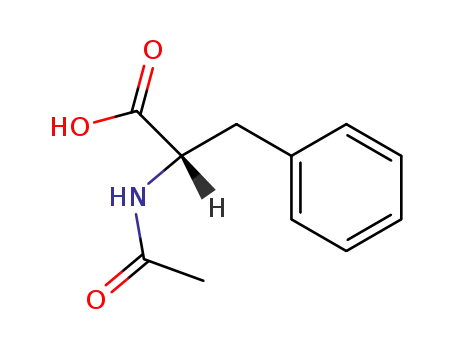
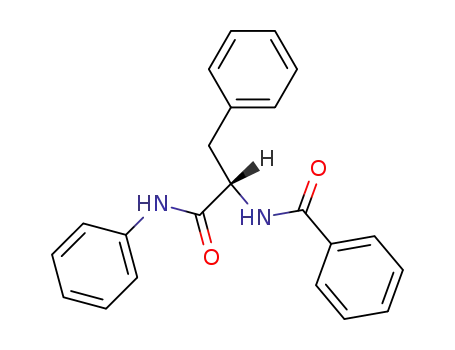
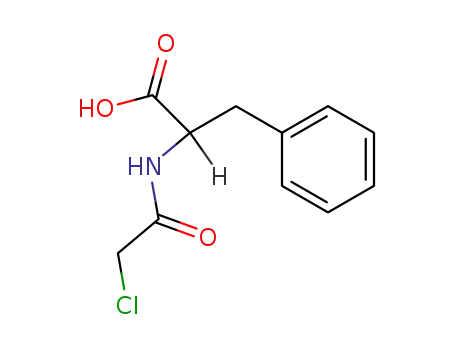
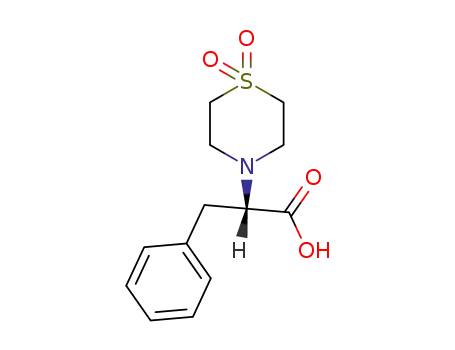
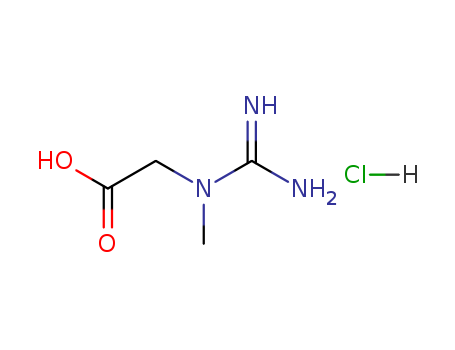
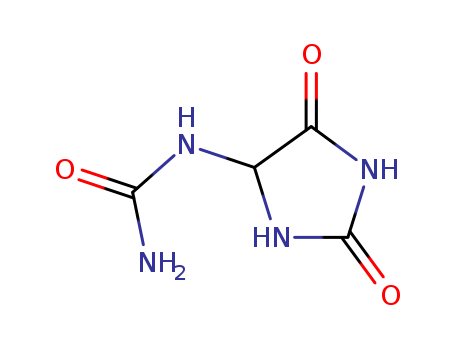
|
Preparation
|
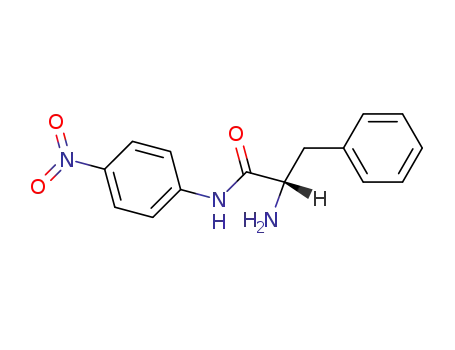
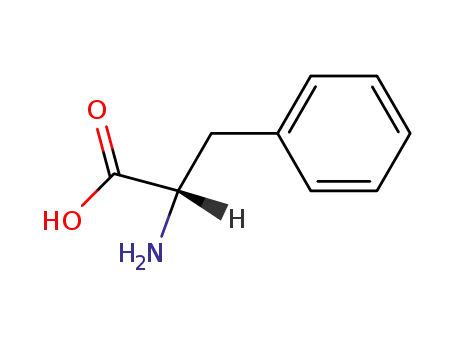
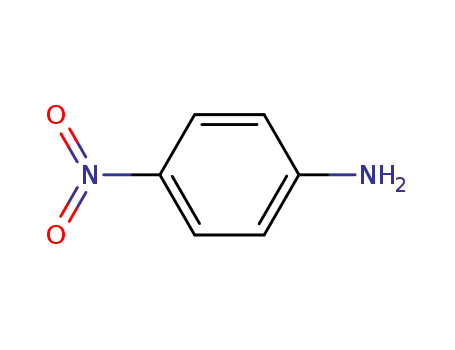
From PTS-negative Escherichia coli bioengineered strains.
|
|
Synthesis Reference(s)
|
Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 29, p. 427, 1951 DOI: 10.1139/v51-051The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 30, p. 3414, 1965 DOI: 10.1021/jo01021a035Tetrahedron Letters, 26, p. 2449, 1985 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)94850-0
|
|
Air & Water Reactions
|
Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are weak acids.
|
|
Reactivity Profile
|
L-Phenylalanine may be light sensitive. Act as weak acids in solution.
|
|
Health Hazard
|
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition L-Phenylalanine emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides.
|
|
Fire Hazard
|
Flash point data for L-Phenylalanine are not available; however, L-Phenylalanine is probably combustible.
|
|
Biochem/physiol Actions
|
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid. It is significantly involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, l-DOPA (Dihydroxyphenylalanine), melanin and thyroxine. L-Phenylalanine metabolism also results in phenylethylamine, that brings about effect of a stimulant in the brain and enhances mood.
|
|
Purification Methods
|
Likely impurities are leucine, valine, methionine and tyrosine. Crystallise L-phenylalanine from water by adding 4volumes of EtOH. Dry it in vacuo over P2O5. Also crystallise it from saturated refluxing aqueous solutions at neutral pH, or 1:1 (v/v) EtOH/water solution, or conc HCl. It sublimes at 176-184o/0.3mm with 98.7% recovery and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2156-2175 1961, Beilstein 14 IV 1552.]
|
|
Precursor of Biochemical Pathways
|
Phenylalanine serves as a precursor for the phenylpropanoid pathway and is essential for the synthesis of melanin, dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), and thyroxine.
|
|
Marker of Disease Severity in COVID-19
|
Serum levels of phenylalanine have been associated with increased inflammation, higher SOFA scores, ICU admission, and mortality rates among COVID-19 patients. Lower serum phenylalanine levels were observed in mild cases compared to moderate and severe cases.
|
|
Role in Age-Related Cardiac Dysfunction
|
Elevated plasma levels of phenylalanine are associated with age-related cardiac dysfunction. Aging leads to increased plasma phenylalanine levels, which may promote cardiac dysfunction. Pharmacological restoration of phenylalanine catabolism has been suggested as a potential therapeutic strategy for age-associated cardiac impairment.
|
|
Personal Health Monitoring During Exercise
|
Phenylalanine fluctuations induced by protein intake during exercise can be tracked, and sweat-blood phenylalanine levels can be analyzed for personal health monitoring. Sweat phenylalanine levels correlate with blood phenylalanine levels and can be used to assess various nutrition and disease statuses, such as phenylketonuria (PKU), muscle protein metabolism during exercise, liver dysfunction in obesity, and viral infection severity.
|
|
Associated with Phenylketonuria (PKU)
|
Phenylalanine metabolism is disrupted in individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), leading to the accumulation of phenylalanine in the brain, which can cause profound and irreversible mental disability if left untreated.
|
|
Definition
|
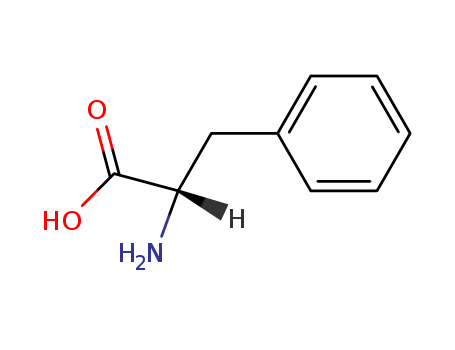
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of phenylalanine.
|
|
General Description
|
Odorless white crystalline powder. Slightly bitter taste. pH (1% aqueous solution) 5.4 to 6.
|
|
Who Evaluation
|
Evaluation year: 2004
|
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego