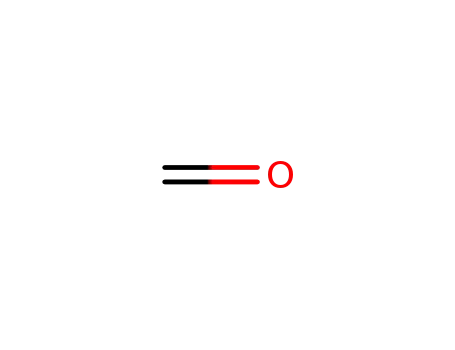|
Description
|
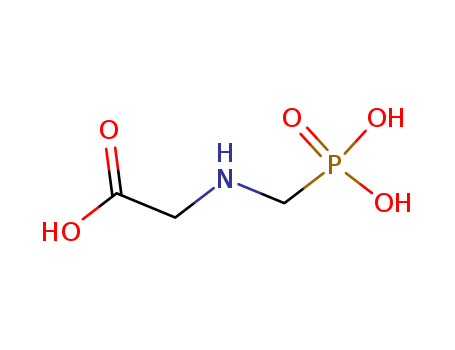
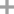
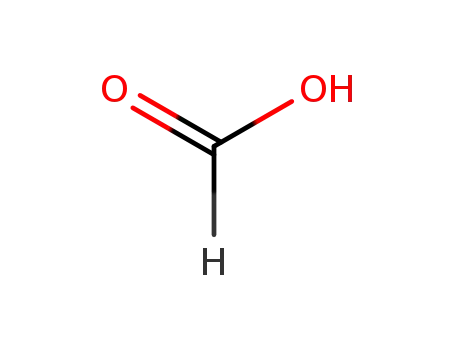
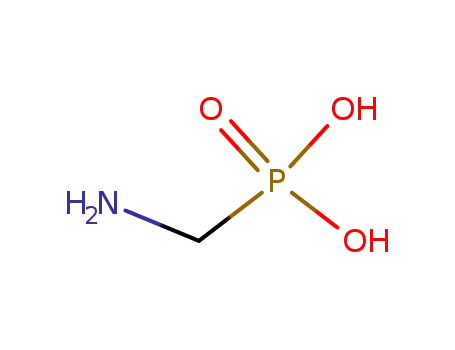
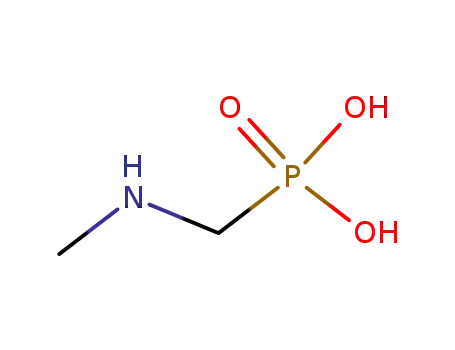
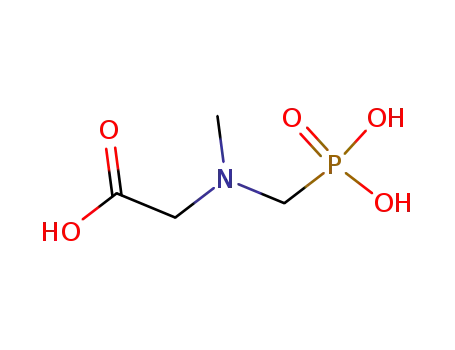
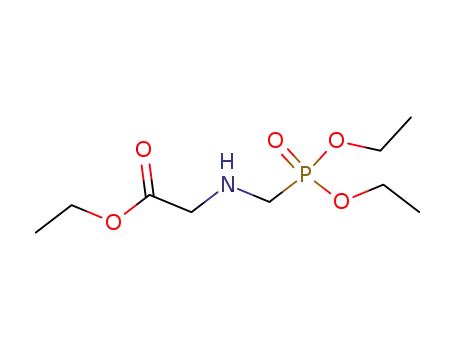
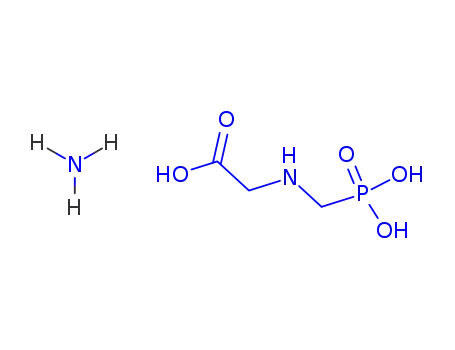
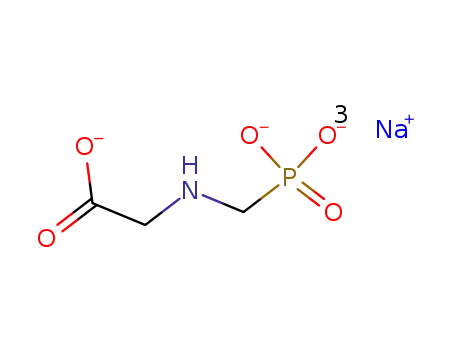
Glyphosate, [N-(phosphonomethyl) glycine], was synthesized in 1950 and patented as a chemical chelator, capable of binding metals such as calcium, magnesium, and manganese. Shanghai Wibson Biotechnology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise that mainly develops and sells pharmaceutical and chemical raw materials and other related products. We have 16 years of experience in R&D and manufacturing, we have rich experience in shipping, many well-known companies have cooperated with us, and are good at shipping various chemical products with us.We can provide OEM,ODM service with low MOQ! |
|
Uses
|
Glyphosate is an active ingredient (a.i.) in very widely used herbicide formulations. Accordingly, the toxicity of glyphosate and glyphosate-based formulations (GBFs) has been extensively studied. Glyphosate is absorbed through plant leaves. It is then carried by the sap stream into the plant roots, where it prevents them from absorbing nutrients from the soil – thereby killing the plant. Annual weeds, including grasses and most broad-leafed plants, are easily controlled using Glyphosate. |
|
Toxicity
|
Acute oral-rat LD50 is 4320mg/kg, acute percutaneous-rabbit LD50> 5000mg/kg (7940mg/kg); it has mild stimulus on skin and eyes of rabbits. Using a dose 2000 mg/kg for feeding rats for 90d causes no abnormal symptoms. Animal tests exhibit no teratogenic, carcinogenic, mutagenic effect. Trout-LC50> 1000mg/L, Daphnia 780mg/L. It has low toxicity to bees and birds.
|
|
Flammability and hazard characteristics
|
combustion produces toxic gases of nitrogen oxides and phosphorus oxides
|
|
Storage characteristics
|
Treasury: ventilation, low-temperature and drying; store separately from food raw material
|
|
Extinguishing agent
|
Dry powder, foam, sand
|
|
Reactivity Profile
|
Glyphosate may react with galvanized steel or unlined steel (except stainless steel) containers to produce hydrogen gas which may form a highly combustible or explosive gas mixture. Glyphosate can react with caustic (basic) materials to liberate heat. Glyphosate is corrosive to iron.
|
|
Fire Hazard
|
Flash point data for Glyphosate are not available; however, Glyphosate is probably combustible.
|
|
Biochem/physiol Actions
|
Glyphosate?(N-[phosphonomethyl] glycine) is the herbicide form of the isopropylamine salt of glyphosate.
|
|
Potential Exposure
|
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this nonselective and nonresidual pre-emergence organophos phate herbicide. Has wide residential use in the United States for the control of weeds.
|
|
Metabolic pathway
|
The photolytic degradation of glyphosate results in the formation of glycine, (aminomethyl)phosphonic acid (AMPA), and NH3. Glyphosate undergoes nitrogen ? carbon cleavage on reaction with m- chloroperoxybenzoic acid, leading ultimately to many of the same products formed on their metabolism and environmental degradation. It is suggested that insoluble complexes of glyphosate with iron(III), copper(II), calcium, and magnesium ions are formed at near-neutral pH, a mechanism of which is the inactivation of glyphosate in contaminated groundwater.268 The bacterium degrades high levels of glyphosate, primarily by converting to AMPA. Appreciable uptake of glyphosate is observed with seedlings and leaves and to a lesser extent with culture cells in the form of non-metabolized glyphosate, with AMPA as the only detectable metabolite.
|
|
Metabolism
|
In soils, glyphosate is rapidly mineralized within 1 to 2 weeks, and degradation occurs under aerobic and anaerobic conditions (79). The C?P bond is relatively resistant to chemical degradation, but several bacteria, e.g., Arthrobacter (80), Pseudomonas (81), various members of the Rhizobiaceae family (82), and certain fungi (83), have been shown to metabolize glyphosate.
|
|
Shipping
|
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz ardous material, Technical Name Required.
|
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego