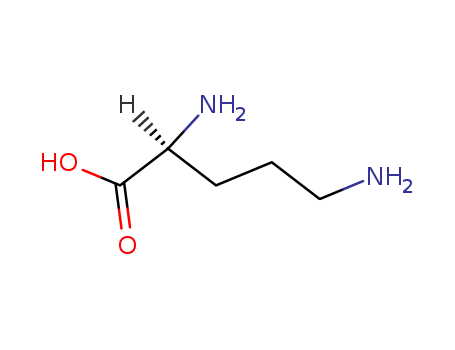
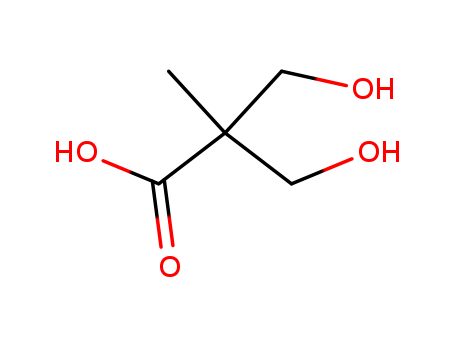
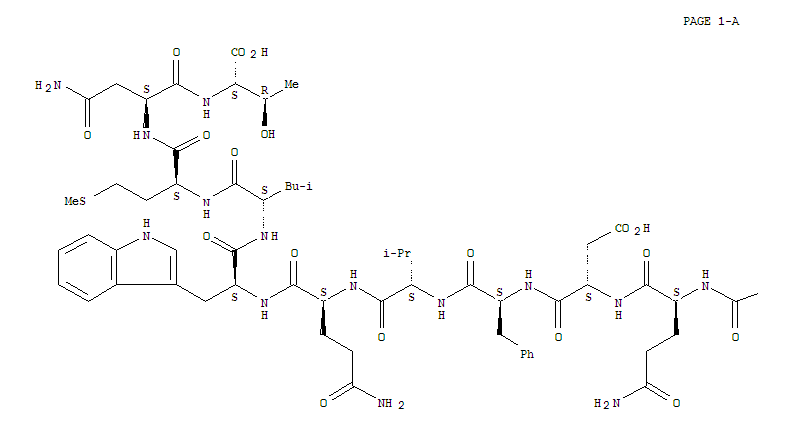
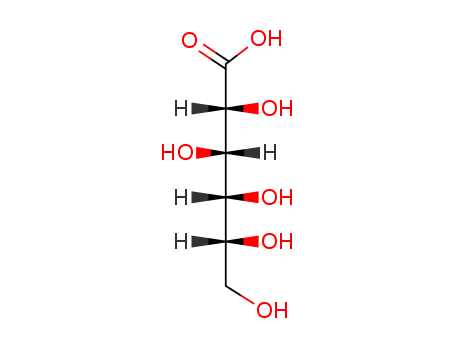
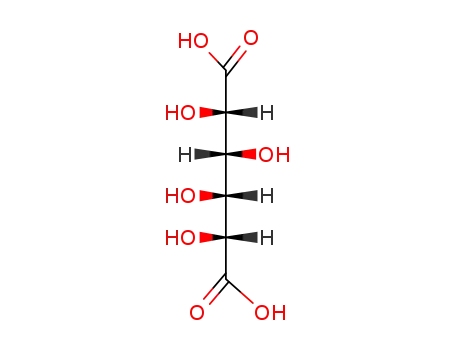
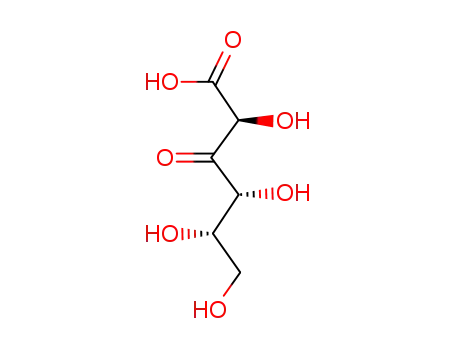
Manufacture of gluconic acid: A review towards process intensification for green production
Parimal Pal , Ramesh Kumar , Subhamay Banerjee
, Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification Volume 104 , June 2016, Pages 160-171
In the recent years, possibility of integration of tailor-made and highly selective membranes and modules with fermenter in downstream purification of gluconic acid appears to have brightened the prospects of gluconic acid manufacture. This paper through a comprehensive review of the critical aspects of production of gluconic acid suggests ways towards development of green processes through process intensification leading to the prospects of sustainable business.
Gluconic acid: Properties, production methods and applications—An excellent opportunity for agro-industrial by-products and waste bio-valorization
Ana M. Cañete-Rodríguez a , Inés M. Santos-Dueñas a , Jorge E. Jiménez-Hornero b , Armin Ehrenreich c , Wolfgang Liebl c , Isidoro García-García a
, Process Biochemistry Volume 51, Issue 12 , December 2016, Pages 1891-1903
This review focuses on d-gluconic acid (GA), a common additive used in pharmaceutical, textile, building and, especially, food industries. GA is usually obtained through biological methods involving the partial oxidation of glucose. This acid provides an excellent example of how some production wastes and surpluses with high carbohydrate contents can be optimally exploited.
Electrical contacting of flavoenzymes and NAD(P)+-dependent enzymes by reconstitution and affinity interactions on phenylboronic acid monolayers associated with Au-electrodes
Zayats, Maya,Katz, Eugenii,Willner, Itamar
, p. 14724 - 14735 (2002)
The preparation of integrated, electrica...
Reinforcing the Induction of Immunogenic Cell Death Via Artificial Engineered Cascade Bioreactor-Enhanced Chemo-Immunotherapy for Optimizing Cancer Immunotherapy
Sun, Kai,Hu, Jinzhong,Meng, Xiangyu,Lei, Yunfeng,Zhang, Xuezhong,Lu, Zhuoxuan,Zhang, Liming,Wang, Zhifei
, (2021)
Traditional chemo-immunotherapy can elic...
Low temperature synthesis of Cu2O crystals: Shape evolution and growth mechanism
Sui, Yongming,Fu, Wuyou,Yang, Haibin,Zeng, Yi,Zhang, Yanyan,Zhao, Qiang,Li, Yangen,Zhou, Xiaoming,Leng, Yan,Li, Minghui,Zou, Guangtian
, p. 99 - 108 (2010)
An interesting shape evolution of Cu2O c...
Crystal structure of human senescence marker protein 30: Insights linking structural, enzymatic, and physiological functions
Chakraborti, Subhendu,Bahnson, Brian J.
, p. 3436 - 3444 (2010)
Human senescence marker protein 30 (SMP3...
A comparative evaluation of the activity modulation of flavo and non-flavo enzymes induced by graphene oxide
Maiti, Susmita,Kundu, Somashree,Roy, Chandra Nath,Ghosh, Debasmita,Das, Tushar Kanti,Saha, Abhijit
, p. 2601 - 2608 (2017)
Graphene, and its water soluble derivati...
KINETICS OF OXIDATION OF D-GLUCOSE BY HEXACHLOROIRIDATE(IV) AND TETRACHLOROAURATE(III)
Gupta, Kalyan Kali Sen,Gupta, Shipra Sen,Chatterejee, Uma,Tarafdar, Archana,Samanta, Tapashi,Shamra, Umashankar
, p. 81 - 88 (1983)
Kinetic data for the oxidation of D-gluc...
Preparation of sulfonated poly(ether-ether-ketone) functionalized ternary graphene/AuNPs/chitosan nanocomposite for efficient glucose biosensor
Singh, Jay,Khanra, Partha,Kuila, Tapas,Srivastava, Manish,Das, Ashok K.,Kim, Nam Hoon,Jung, Bong Joo,Kim, Da Yeong,Lee, Seung Hee,Lee, Dong Won,Kim, Dae-Ghon,Lee, Joong Hee
, p. 1724 - 1735 (2013)
A facile method of preparing water-dispe...
One-pot biocatalytic conversion of lactose to gluconic acid and galacto-oligosaccharides using immobilized β-galactosidase and glucose oxidase
Todea, Anamaria,Benea, Ioana Cristina,B?tcan, Ioan,Péter, Francisc,Klébert, Szilvia,Feczkó, Tivadar,Károly, Zoltán,Biró, Emese
, p. 202 - 211 (2021)
One-pot cascade reaction systems offer s...
Pd(ii) nanoparticles in porous polystyrene: Factors influencing the nanoparticle size and catalytic properties
Tsvetkova, Irina B.,Matveeva, Valentina G.,Doluda, Valentin Y.,Bykov, Alexei V.,Sidorov, Alexander I.,Schennikov, Sergey V.,Sulman, Michael G.,Valetsky, Pyotr M.,Stein, Barry D.,Chen, Chun-Hsing,Sulman, Esther M.,Bronstein, Lyudmila M.
, p. 6441 - 6448 (2012)
In this paper for the first time we pres...
Preparation of Au-Pd/C catalysts by adsorption of metallic species in aqueous phase for selective oxidation
Hermans, Sophie,Deffernez, Aurore,Devillers, Michel
, p. 77 - 82 (2010)
Au/C and Au-Pd/C catalysts were prepared...
Nanocomposite incorporating V2O5 nanowires and gold nanoparticles for mimicking an enzyme cascade reaction and its application in the detection of biomolecules
Qu, Konggang,Shi, Peng,Ren, Jinsong,Qu, Xiaogang
, p. 7501 - 7506 (2014)
Artificial enzyme mimics are a current r...
Catalytic deep eutectic solvents for highly efficient conversion of cellulose to gluconic acid with gluconic acid self-precipitation separation
Liu, Feijie,Xue, Zhimin,Zhao, Xinhui,Mou, Hongyu,He, Jing,Mu, Tiancheng
, p. 6140 - 6143 (2018)
A family of FeCl3·6H2O based catalytic d...
Enhanced photocatalytic performance for oxidation of glucose to value-added organic acids in water using iron thioporphyrazine modified SnO2
Zhang, Quanquan,Ge, Yanchun,Yang, Changjun,Zhang, Bingguang,Deng, Kejian
, p. 5019 - 5029 (2019)
The selective conversion of glucose into...
Influence of the ionic liquid presence on the selective oxidation of glucose over molybdenum based catalysts
Megías-Sayago,Carrasco,Ivanova,Montilla,Galindo,Odriozola
, p. 82 - 90 (2016)
Two different approaches are proposed in...
A new route to the considerable enhancement of glucose oxidase (GOx) activity: The simple assembly of a complex from CdTe quantum dots and GOx, and its glucose sensing
Cao, Lihua,Ye, Jian,Tong, Lili,Tang, Bo
, p. 9633 - 9640 (2008)
A new complex consisting of CdTe quantum...
Mesoporous carbon-confined Au catalysts with superior activity for selective oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid
Ma, Chunyan,Xue, Wenjuan,Li, Jinjun,Xing, Wei,Hao, Zhengping
, p. 1035 - 1041 (2013)
A series of ordered mesoporous carbon (O...
Real-time monitoring of mass-transport-related enzymatic reaction kinetics in a nanochannel-array reactor
Li, Su-Juan,Wang, Chen,Wu, Zeng-Qiang,Xu, Jing-Juan,Xia, Xing-Hua,Chen, Hong-Yuan
, p. 10186 - 10194 (2010)
To understand the fundamentals of enzyma...
A Sweet H2S/H2O2Dual Release System and Specific Protein S-Persulfidation Mediated by Thioglucose/Glucose Oxidase
Li, Xiaolu,Ni, Xiang,Qian, Wei-Jun,Shen, Tun-Li,Xian, Ming
, p. 13325 - 13332 (2021/09/03)
H2S and H2O2 are two redox regulating mo...
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego