|
Sources and Categories
|
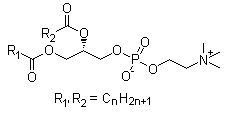
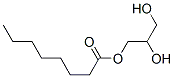
Lecithin is a complex mixture of phosphatides, primarily phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylinositol, with varying amounts of triglycerides, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. It is isolated from animal or vegetable sources, with main sources being maize, egg yolk, and soybean.
|
|
Chemical Composition and Structure
|
Lecithin is composed of phosphatides, predominantly phosphatidylcholine, along with other phospholipids, triglycerides, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. Its molecular structure is amphiphilic, allowing it to exhibit excellent emulsifying properties.
|
|
Mechanism of Action
|
Lecithin acts as an emulsifier, modifying crystal habit (size), and interacts with wax molecules to alter the morphology and dimensions of fat crystals. It also self-assembles through non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, in food products.
Lecithin exhibits excellent emulsifying properties due to its amphiphilic molecular structure. It's main component, phosphatidylcholine, plays a crucial role in cell membrane formation and serves as a regulatory molecule in various biological processes.
Lecithin is metabolized to choline, which can generate the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, promoting cell activation and neural network flexibility.
|
|
Medical Applications
|
Lecithin has been reported to improve cardiovascular health by preventing cholesterol deposition, enhance immune and liver functions, and improve skin texture. Choline derived from lecithin hydrolysis can promote cell activation and neural network flexibility.
|
|
Industrial Applications
|
Used as an emulsifier in food products like margarine, chocolate, cakes, and breads, and in personal care products. Also utilized in livestock and poultry feed industry to enhance production performance, nutrient digestibility, and health status. Lecithin nanoparticles coated with chitosan serve as nanocarriers for bioactive compounds, improving their stability, release, and effectiveness.
|
|
Production Methods
|
Commercial lecithin is isolated through hydration of solvent-extracted oils from sources like soy, safflower, or corn. It can be further processed by hydrogenation or enzymatic modification. Industrial production involves bleaching, if desired, by hydrogen peroxide and benzoyl peroxide, and drying by heating. Enzyme-modified lecithin, such as lysolecithin, is prepared by treating lecithin with phospholipase A2 or pancreatin.
|
|
Definition
|
ChEBI: A glycerophosphocholine compound having O-acyl substituents at both the 1- and 2-positions of the glycerol. It is a major constituent of cell membranes.
|
|
Biochem/physiol Actions
|
It also acts as a source of lipid messengers/ bioactive lipids including: lysophosphatidylcholine, diacylglycerol, phosphatidic acid, lysophosphatidylcholine, arachidonic acid and platelet activating factor. Phosphatidylcholine is produced in the liver by the CDP-choline (cytidine diphosphocholine) pathway.
|
|
Safety
|
Lecithin is a component of cell membranes and is therefore consumed as a normal part of the diet. Although excessive consumption may be harmful, it is highly biocompatible and oral doses of up to 80 g daily have been used therapeutically in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia. When used in topical formulations, lecithin is generally regarded as a nonirritant and nonsensitizing material. The Cosmetic Ingredients Review Expert Panel (CIR) has reviewed lecithin and issued a tentative report revising the safe concentration of the material from 1.95% to 15.0% in rinse-off and leave-in products. They note, however, that there are insufficient data to rule on products that are likely to be inhaled.
|
|
Incompatibilities
|
Incompatible with esterases owing to hydrolysis.
|
|
Who Evaluation
|
Evaluation year: 1980
|
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego